LoRaWAN®
LoRaWAN® – short for Long Range Wide Area Network – describes the network structure and the protocol used to ensure standardised communication between network participants. LoRaWAN® ensures the manufacturer-independent use of solutions within a network or across different networks and also allows new solutions to be easily integrated into existing networks.
LoRa®
LoRa® refers to the radio technology used for data transmission, i.e. the basic mode of communication. A special modulation process for transmitting information ensures smooth processes and protects against interference, such as interference from sensors transmitting at the same time.
Basic information:
Originally developed for the Internet of Things (IoT), LoRaWAN® wireless technology is increasingly being promoted by cities, municipalities, property managers and energy suppliers. As an alternative to other wireless systems such as Zigbee or Bluetooth®, LoRaWAN® is a high-performance solution, especially where long ranges and high efficiency are essential.
LoRaWAN® has a wide range of applications. It is a particularly powerful solution for less time-critical applications such as temperature or humidity measurements. From the operator's point of view, compliance with high security standards through double-encrypted data transmission and the possibility of Europe-wide use without incurring licence costs are convincing. Thermokon's LoRaWAN® product portfolio offers the flexibility to choose between battery-powered and wired sensors with analogue signal outputs and LoRaWAN® option. In battery operation, the high energy efficiency of the sensors ensures extremely low-maintenance operation over many years.
The fact that LoRaWAN® is very popular worldwide is due to the wide range of applications and opportunities offered by this relatively new technology. LoRaWAN® not only offers enormous savings potential thanks to the low costs involved in setting up the network, but also makes a significant contribution to cost-efficient utilisation for various applications.
In addition to the classic integration of sensors in the control of ventilation systems, for example, the LoRaWAN® interface offers the possibility of sending live data to a cloud independently of the building management system – this serves as a data basis for preventive maintenance.
Functional principle:
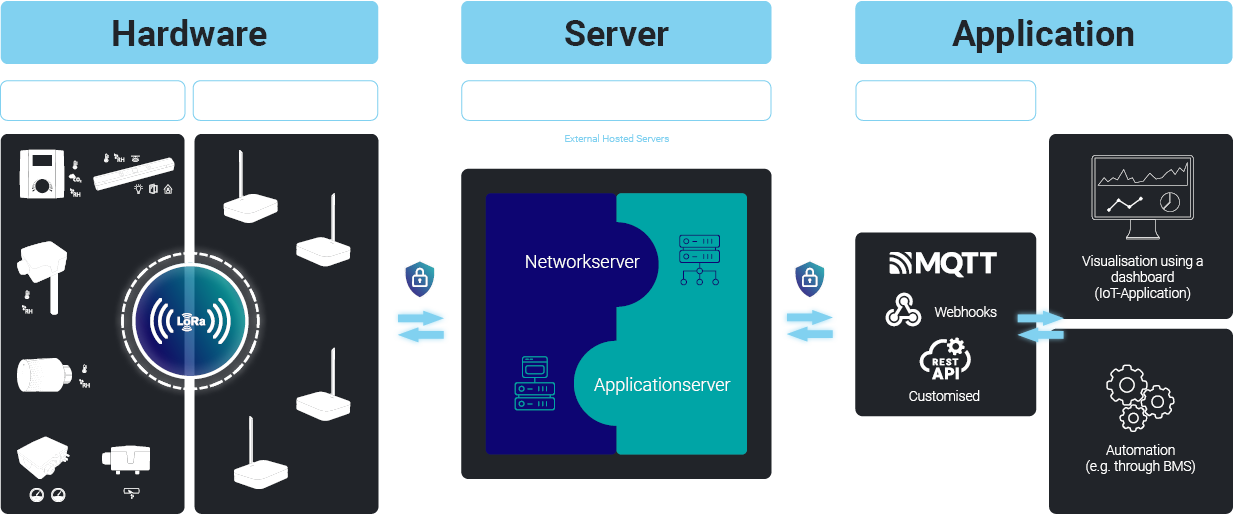
The LoRaWAN® network is based on a multi-level architecture in which sensors, actuators, gateways, network and application servers and, if necessary, converters work together to efficiently collect, transmit and process sensor data and integrate it into existing systems such as IoT platforms or building management systems (BMS).
Step 1 – Sensors and Actuators (end devices):
Are, for example, LoRaWAN® sensors that record measured values and send AES128 encrypted data to a gateway.
Step 2 – Gateways:
Receive the data from the various end devices and pass it on (still encrypted) to the network server (standard IP connection). Each gateway forwards all received data to the network server. In this way, several hundred to approx. 1,000 wireless sensors can be connected via one gateway. To cover larger areas, several gateways are connected to the same network server.
Cloud Connectivity
Integration into IoT platforms via network and application servers.
Step 3 – Network / Application Server:
The central LoRaWAN® network server collects data from its gateways and forwards it for further processing. Duplicate data packets are discarded. The network server decrypts the data and forwards it to the respective application server.
The application server processes and decodes the data according to the specific needs of the application, enabling seamless integration into external systems such as cloud-based IoT platforms, databases, or user interfaces. Raw sensor data is translated into meaningful information, processed in line with defined business rules and formats the data for further use.
Step 4 – Application:
At the application level, the processed data is used to drive decision-making, optimize operations, and enhance the user experience. Applications may visualize the data in dashboards, enable predictive analytics, or integrate with third-party IoT platforms. These platforms can also provide insights, trigger automated workflows, or send notifications and alerts based on predefined conditions.
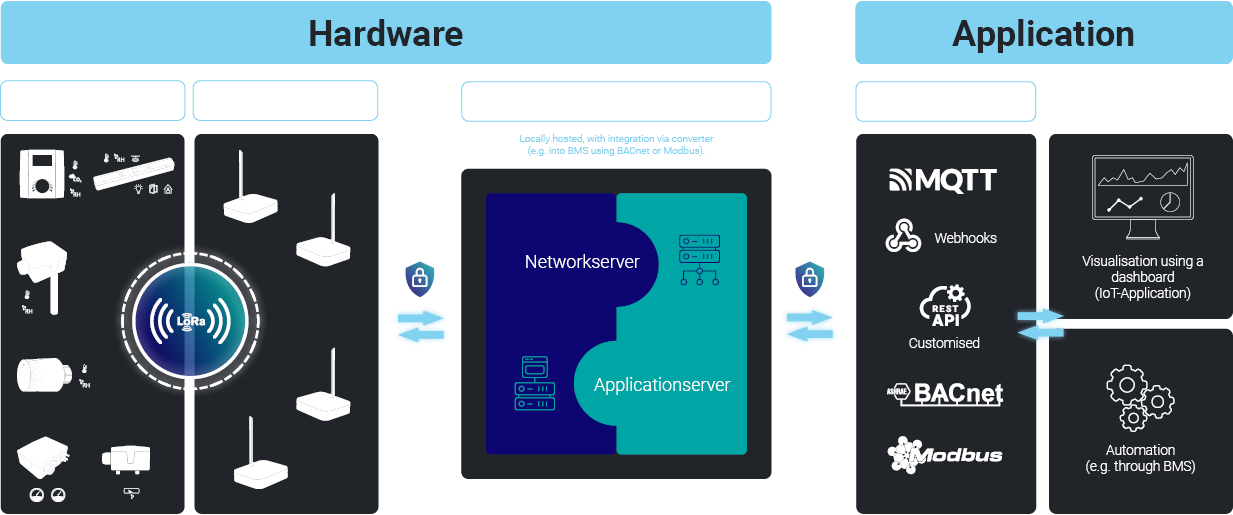
Building Management System (BMS) Integration
Protocol conversion and integration into the (existing) BMS.
Step 3 – Converter:
The converter combines the network and application server into a single device while also handling protocol conversion. It directly converts LoRaWAN® data to Modbus TCP/IP and BACnet IP, enabling seamless integration with a Building Management System (BMS).
External LoRaWAN® gateways serve as wireless receivers and can be connected to the converter for efficient data transmission.
Step 4 – BMS Integration:
At the BMS integration level, the converted data is used for monitoring, automation, and optimization of building operations. The system enables visualization, predictive maintenance, and automated control of HVAC, lighting, and other infrastructure.
By directly integrating into the BMS via common building automation protocols such as Modbus TCP/IP and BACnet IP, the solution improves efficiency, sustainability, and operational insights, while ensuring seamless interoperability in modern (smart) IoT environments.


 Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Deutschland)  English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom) 